- Home
- > The Marketix Blog
- > SEO
History of SEO: A Long Journey

SEO, or Search Engine Optimisation, is a crucial part of digital marketing, enabling websites to rank higher on search engines and attract organic traffic. As we stand in 2024, we've come a long way. SEO has evolved significantly since its early days, adapting to changing algorithms and user behaviours.
From its humble beginnings to the sophisticated strategies of today, SEO has undergone remarkable changes. Key developments, major algorithm updates, and shifts in best practices have shaped its journey.
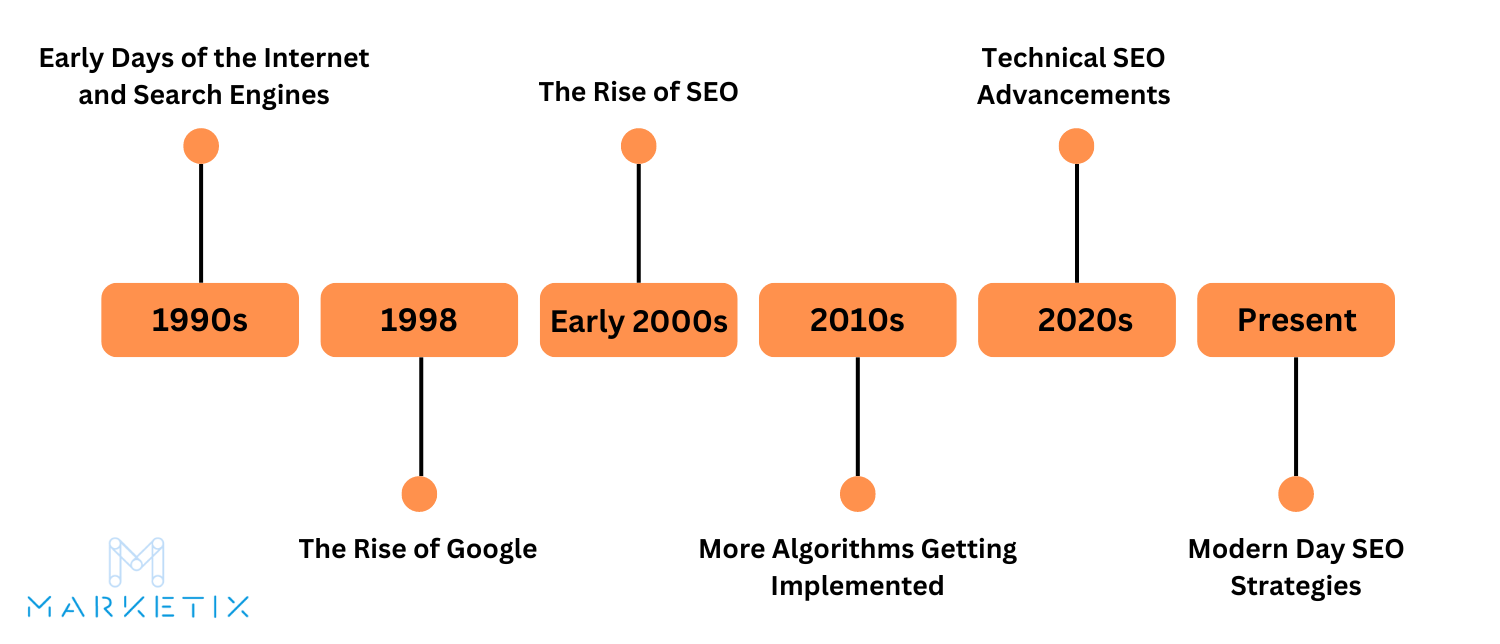
The Early Days of the Internet and Search Engines
The 1990s marked the birth of the internet, a period that transformed communication and information sharing.
Early users accessed the web through simple text-based interfaces. As more people connected, the need to organise and find information grew. This demand led to the creation of the first search engines, which were rudimentary compared to today's standards.
Archie, developed in 1990, was the first tool for indexing FTP archives, allowing users to find specific files. Gopher followed, providing a system for organising and searching text files. In 1991, Tim Berners-Lee revolutionised the internet by creating the World Wide Web. This new system used hypertext to link documents, making it easier to navigate the growing web.
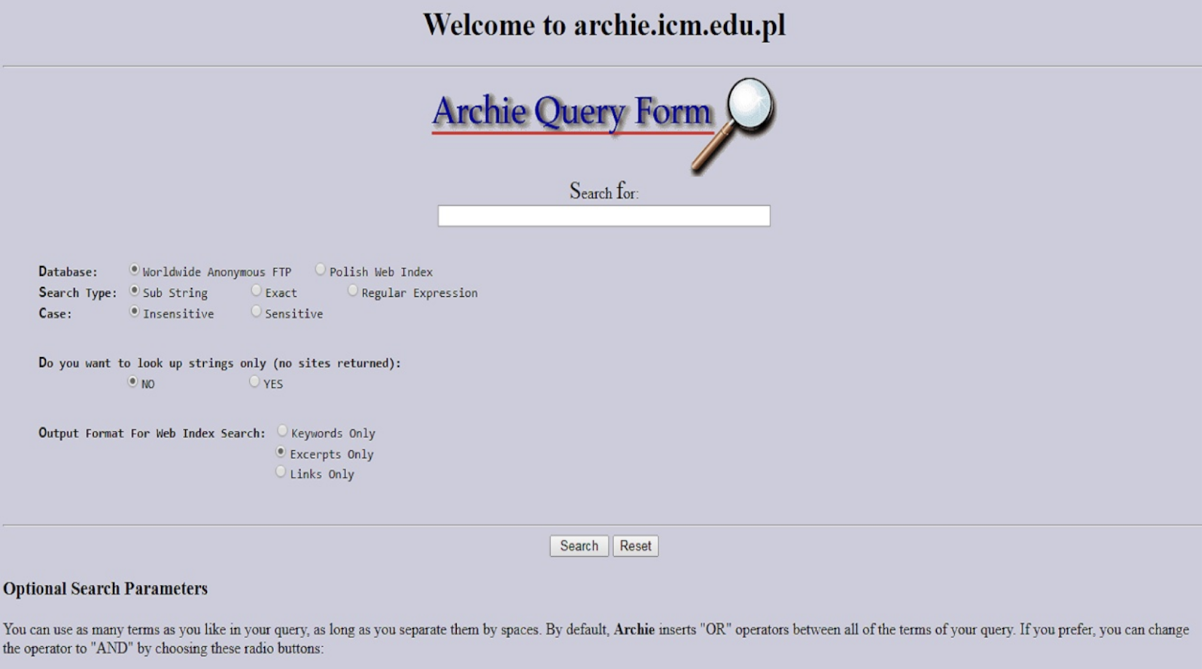
The introduction of the World Wide Web spurred the development of web directories and search engines to help users find information. Early directories like Yahoo! listed websites by category, while search engines began using algorithms to index and retrieve relevant pages. Excite, launched in 1993, was one of the first search engines to use keyword-based indexing, a foundational concept for future SEO practices.
By the mid-1990s, several search engines had emerged, each improving on the previous models. Lycos, launched in 1994, offered a comprehensive index of web pages and became one of the most popular search engines of the time. AltaVista, introduced in 1995, brought advanced features like natural language queries and included a large database of indexed pages.
These early search engines laid the groundwork for more sophisticated technologies, shaping the way people accessed information online.
As search engines evolved, the need for more effective indexing and retrieval methods became apparent. Web crawlers, also known as spiders or bots, were developed to automate the process of indexing web pages.
Crawlers navigated the web by following links from page to page, collecting data to build searchable indexes. It was a crucial innovation for handling the rapidly expanding web, allowing search engines to provide more relevant results to users.
The basic principles of web crawling and indexing remain central to modern SEO.
The late 1990s saw a rapid expansion of the internet, with more websites and users coming online every day. This growth highlighted the limitations of early search engines, which often returned irrelevant or low-quality results.
The emergence of Google in 1998 marked a significant turning point. Founded by Larry Page and Sergey Brin, Google introduced the PageRank algorithm, which ranked pages based on the number and quality of links pointing to them. This approach revolutionised search by prioritising relevance and authority, setting new standards for search engine performance.
The innovations of the 1990s laid the foundation for modern SEO. Early search engines and indexing methods provided the tools needed to navigate the web's vast information landscape. The creation of the World Wide Web and the development of web crawlers and algorithms set the stage for more advanced search technologies.
As we moved into the 2000s, these early developments would evolve into the sophisticated SEO strategies we use today.
The Rise of Google
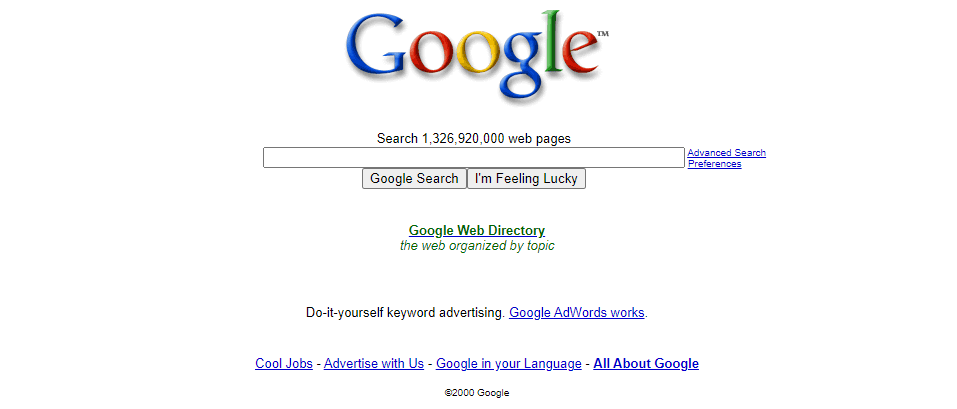
In 1998, Larry Page and Sergey Brin, two Stanford University students, founded Google. Their vision was to create a search engine that provided more accurate and relevant results than existing ones. They achieved this with the development of the PageRank algorithm. PageRank analysed the web's link structure to determine the importance of each page.
Unlike other search engines, which relied heavily on keyword frequency, Google assessed the quality and quantity of links pointing to a page. This innovative approach quickly set Google apart from its competitors.
The introduction of the PageRank algorithm was revolutionary. It shifted the focus from merely matching keywords to understanding the web's structure and relationships.
As a result, users received more relevant and higher-quality search results. This new standard of search accuracy propelled Google to the forefront of the search engine market. Within a few years, it became the dominant search engine, surpassing established players like Yahoo! and AltaVista.
Google's rise to dominance was also driven by its clear mission: to organise the world's information and make it universally accessible and useful.
Google continuously refined its algorithms to improve search quality and user experience. Features like personalised search results, universal search (integrating different types of content), and the Knowledge Graph enhanced the relevance and richness of search results. Google's commitment to improving its search engine helped it maintain a competitive edge.
The impact of Google on the search engine landscape was profound. Its success forced other search engines to adopt similar ranking methodologies, leading to a more competitive and innovative industry.
Google's influence extended beyond search, shaping the broader internet ecosystem. The emphasis on link quality and relevance influenced website design, content creation, and digital marketing strategies. SEO practices evolved to align with Google's standards, prioritising high-quality content and user experience.
Google's dominance and continuous innovation set the stage for the future of search and digital marketing.
The Birth of SEO
The birth of SEO in the late 1990s saw the emergence of techniques aimed at improving website visibility on search engines.
Early SEO methods were simple and often crude by today's standards. Keyword stuffing was a common practice, where webmasters loaded pages with repetitive keywords in an attempt to rank higher.
On-page optimisation included efforts to improve content and structure, making pages more accessible and appealing to both users and search engines.
Webmasters played a crucial role in the early days of SEO. They were responsible for maintaining and optimising websites and experimenting with various techniques to improve search rankings. Their efforts were driven by a growing understanding of search engine algorithms and how to influence them. However, the lack of formal guidelines led to a trial-and-error approach.
Some webmasters focused on creating valuable content and improving site architecture. Others, however, resorted to manipulative practices to gain quick results.
Initial misconceptions about SEO were widespread. Many believed that simply increasing keyword density or acquiring numerous low-quality backlinks would guarantee high rankings.
Techniques such as cloaking (showing different content to search engines and users), link farms, and hidden text were employed to deceive search engines.
As search engines evolved, they began to penalise such practices, emphasising the need for ethical SEO.
Case studies from the early days of SEO illustrate both successes and failures. One notable success was the early optimisation of sites like Amazon and eBay, which focused on user-friendly design and valuable content.
On the other hand, several high-profile failures underscored the risks of black-hat techniques. For instance, BMW's German website was temporarily removed from Google's index in 2006 due to the use of doorway pages, a manipulative SEO tactic. This incident highlighted the importance of adhering to search engine guidelines.
These early experiments and experiences shaped the future of SEO. They underscored the necessity of ethical practices and a user-centric approach. The evolution of search engine algorithms continually adjusted to combat manipulative tactics and reward genuine, high-quality content.
As SEO matured, it became clear that long-term success required a commitment to best practices and continuous adaptation to changing search engine behaviours. By 2024, the industry had evolved significantly, embracing more sustainable and user-friendly strategies.
Initial Google Updates
The early 2000s marked the introduction of Google's first major algorithm updates, beginning with the Florida Update in 2003, targeting websites that use manipulative SEO practices, such as keyword stuffing and hidden text.
Many sites that relied on these black-hat techniques saw significant drops in their rankings. The Florida Update was a turning point, signalling Google's commitment to improving search quality and user experience. It forced webmasters to rethink their strategies and adopt more ethical practices.
Following the Florida Update, Google released several other significant updates:
- Jagger (2005): Focused on eliminating spammy backlinks and penalising link farms.
- Bourbon (2005): Aimed at improving search quality by addressing duplicate content and low-quality pages.
- Big Daddy (2006): Enhanced Google's infrastructure to better handle indexing and crawling, improving the overall search experience.
The crackdown on black-hat techniques led to the emergence of white-hat SEO, which prioritised user-focused content and legitimate link-building. Webmasters increasingly adopted best practices to align with Google's evolving standards, marking a significant shift towards sustainable and ethical SEO strategies.
Evolution of Google's Algorithm
Google's algorithm has evolved significantly over the years, with numerous updates aimed at improving search quality and user experience. Each major update has had a profound impact on SEO strategies and best practices.
Panda Update (2011)
- Targeted low-quality content and thin sites
- Penalised content farms and sites with high ad-to-content ratios
- Emphasised the importance of high-quality, unique content
Penguin Update (2012)
- Focused on combating spammy link practices
- Penalised sites using manipulative link schemes
- Encouraged natural link building and quality backlinks
Hummingbird Update (2013)
- Enhanced search precision and semantic search capabilities
- Improved understanding of user intent and context
- Prioritised content relevance and meaning over exact keyword matches
Mobilegeddon (2015)
- Prioritised mobile-friendly websites in search results
- Encouraged responsive design and mobile usability
- Addressed the growing trend of mobile internet usage
RankBrain (2015)
- Introduced machine learning to process search queries
- Improved handling of complex and ambiguous queries
- Highlighted the importance of user intent and behaviour
Medic Update (2018)
- Affected health, medical, and YMYL (Your Money or Your Life) websites
- Emphasised E-A-T (Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness)
- Encouraged high-quality, authoritative content in sensitive niches
BERT (2019)
- Enhanced natural language processing (NLP) capabilities
- Improved understanding of context and nuances in search queries
- Helped deliver more relevant search results for complex queries
Core Web Vitals (2020)
- Focused on user experience metrics: loading, interactivity, and visual stability
- Encouraged improvements in page speed, responsiveness, and visual layout
- Highlighted the importance of technical SEO and user experience
Each update has driven significant changes in SEO strategies.
The evolution of Google's algorithm has consistently shifted towards enhancing user experience and content quality. SEO strategies have had to adapt, focusing more on creating valuable, relevant content and ensuring a positive user experience.
Technical SEO Advancements
Technical SEO is important in modern search optimisation. It ensures that websites are easily crawled and indexed by search engines, which is essential for achieving high rankings.
Over the years, technical SEO practices have evolved significantly. Early efforts focused on basic elements like site structure and internal linking. Today, they encompass advanced techniques such as site speed optimisation, mobile-friendliness, and schema markup.
Site speed has become a critical factor, with faster sites providing better user experiences and higher rankings. Mobile-friendliness has also gained importance, especially after Google's mobile-first indexing. Schema markup, a form of structured data, helps search engines understand content better, leading to rich results in SERPs.
The implementation of HTTPS has been another significant advancement, enhancing security and trustworthiness. Accelerated Mobile Pages (AMP) improve mobile loading speeds, further boosting user engagement.
AI and machine learning are transforming SEO. Algorithms now better understand user intent and deliver more relevant results. Tools like Google's RankBrain and BERT exemplify this shift, focusing on natural language processing and contextual understanding. These technologies have refined how search engines evaluate content quality and relevance.
Several tools and technologies have shaped technical SEO. Google Search Console and Analytics provide valuable insights into site performance and user behaviour. Crawling tools like Screaming Frog help identify technical issues. Platforms like SEMrush and Ahrefs offer comprehensive SEO analysis and reporting.
Local SEO and the Mobile Revolution
The rise of local search transformed how businesses reached nearby customers. Local SEO became vital, allowing small businesses to compete in their local markets.
Impact of the Mobile Revolution on SEO Strategies:
- Increase in mobile device usage changed how people searched online.
- Mobile-friendly websites became crucial for maintaining search rankings.
- Mobile-specific search behaviours, such as voice search, influenced SEO tactics.
Google's Focus on Mobile-First Indexing:
- In 2018, Google shifted to mobile-first indexing, prioritising mobile versions of websites.
- Emphasis on responsive design and mobile usability to ensure better rankings.
- Impact on website speed, user experience, and accessibility.
The Role of Google My Business and Local Citations:
- Google My Business became essential for local SEO, providing business information directly in search results.
- Importance of accurate NAP (Name, Address, Phone Number) details across all platforms.
- Local citations and reviews influenced local search visibility.
Case Studies of Successful Local SEO Campaigns:
- Write a line about the pro fit insulation case study here
- Marketix Digital's case study with Graham and Sons Plumbing achieved top 3 rankings for nearly every suburb in Sydney, over 176 keywords in the top 3 search results, and a significant increase in leads and conversions.
Businesses that embraced these changes saw substantial benefits, reinforcing the need for effective local SEO strategies.
The Future of SEO
The future of SEO is shaped by emerging trends such as voice search, visual search, and AI.
As search algorithms evolve, they will likely prioritise user intent and experience even more. Staying up-to-date with best practices is important for maintaining visibility.
SEO will continue to play a significant role in digital marketing, adapting to new technologies and user behaviours. Industry experts such as Shoaib Mughal, Managing Director of Marketix Digital, predict that personalisation and real-time data will become more important, making SEO an ever-evolving field that demands continuous learning and adaptation.
"Personalisation and real-time data are set to revolutionise the SEO landscape, requiring constant learning and adaptation," says Shoaib Mughal, Managing Director of Marketix Digital. "As these elements become more critical, the field of SEO will continue to evolve at a rapid pace."
References and Further Reading
For more information on SEO and related topics, please refer to the following resources:
Google Search Ranking Systems - https://marketixdigital.com.au/blog/google-search-ranking-systems/
What is SEO? - https://marketixdigital.com.au/blog/what-is-seo/
What Are Backlinks? - https://marketixdigital.com.au/blog/what-are-backlinks/
Common SEO Mistakes - https://marketixdigital.com.au/blog/common-seo-mistakes/
Mobile-First Indexing - https://marketixdigital.com.au/blog/mobile-first-indexing/
The Power of Search Intent - https://marketixdigital.com.au/blog/power-of-search-intent/
Recent Posts

Free Download SEO Book
Download our 24-page SEO book to learn:
- How SEO Really Works
- How to Rank #1
- Content & SEO
- Choosing an SEO Agency
Thank you!
You have successfully joined our subscriber list.
Recent Posts





