- Home
- > The Marketix Blog
- > SEO
What is Search Intent?
Search intent, also known as user intent, is the purpose behind a user's search query. It is what the user hopes to achieve when typing a phrase into a search engine.
Consider a person needing a plumber urgently. They might search for "emergency plumbing in Australia" indicating a need for immediate assistance, likely from the closest available service.
Alternatively, someone might search for the "best plumber in Australia." This suggests they seek reviews or recommendations to find the top-rated service provider.
Imagine John, a homeowner with a burst pipe at midnight. He quickly searches "emergency plumbing" on his phone. He needs a fast solution and clicks on the first local plumber available. His search intent is clear: urgent service.
Conversely, Gina, who plans to renovate her bathroom next month, searches for "best plumber in Australia." She has time to compare services and wants to find the most reliable plumber. Her intent is to make an informed decision based on quality and reputation.
Why Is Search Intent Important in SEO?
Search engines' sophisticated algorithms are designed to deliver the most relevant and high-quality results to users.
Google, for example, dominates the search engine market, holding over 90.91% of the global market share. As a result, businesses aiming to optimise their websites focus primarily on ranking well on Google.
This emphasis on delivering optimal search results means that Google prioritises understanding and satisfying user intent.
When users find what they are looking for quickly and efficiently, they are more likely to return to Google for future searches. Consequently, aligning your website content with user search intent is very important for improving your rankings.
However, this isn't just about appeasing Google. Businesses benefit significantly from aligning their content with search intent. When users find relevant and valuable information on a website, they are more likely to engage, convert, and return.
It’s a win-win situation for both Google and businesses.
Something To Keep In Mind:
High-quality content is a Google top-ranking factor. It meets the needs of users by providing valuable, relevant, and comprehensive information. Google’s ranking factors include:
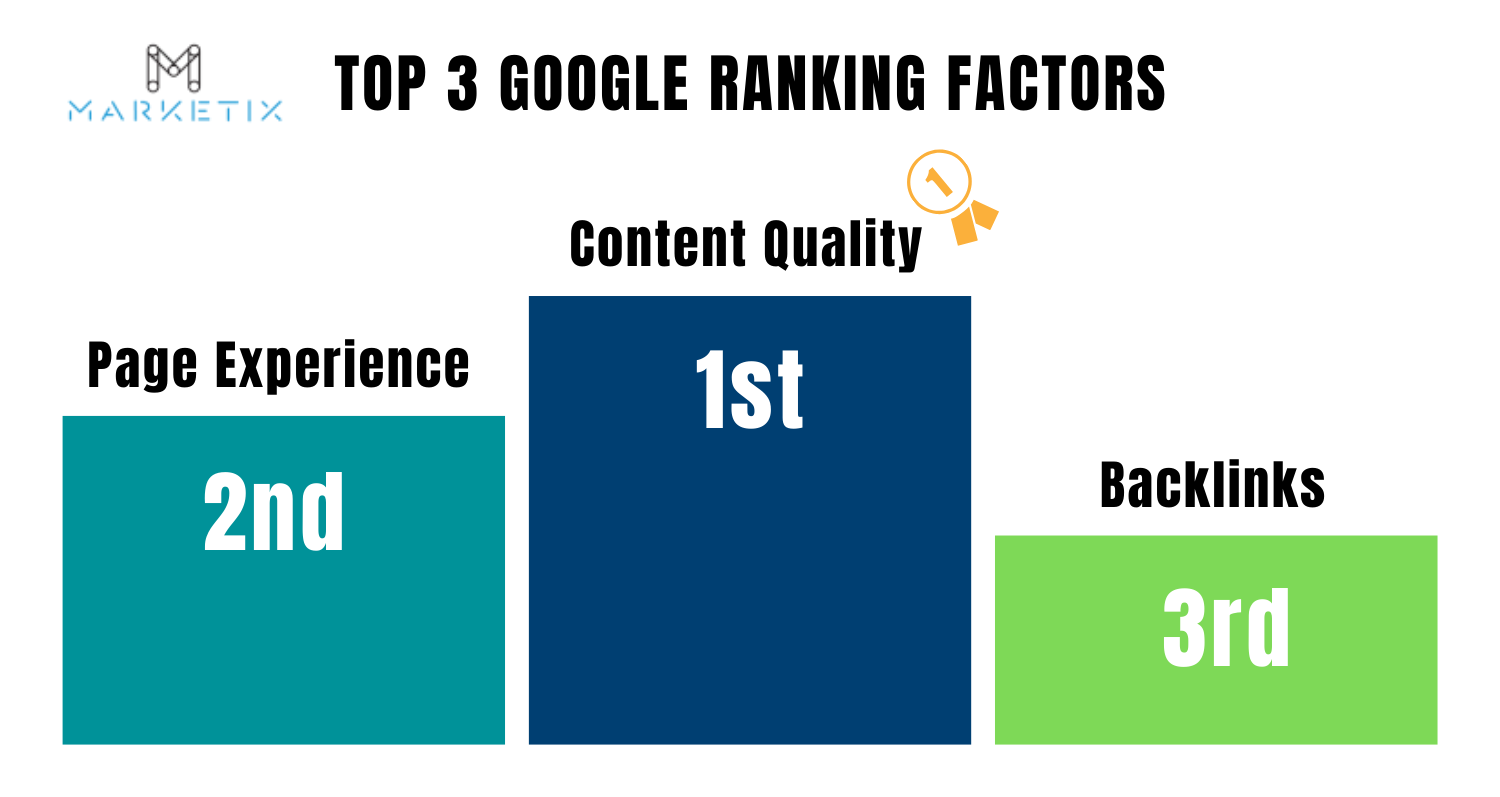
- Content Quality: Content must be informative, well-researched, and tailored to meet the user's intent.
- Page Experience: This includes factors such as page load speed, mobile-friendliness, and interactivity.
- Backlinks: Backlinks are from other websites that point to your content. They serve as endorsements of your content’s credibility and relevance.
Consider a business that offers financial consulting services. They target potential clients searching for "how to manage personal finances" and "best financial advisors near me."
For the first search, the business creates a detailed guide on personal finance management, which is thorough, actionable, and addresses common financial challenges.
For the second search, they provide a list of top-rated financial advisors, complete with reviews, credentials, and contact information.
In this scenario, the business aligns its content with the search intent of different users and makes sure that both types of users find what they need.
When writing content, always align it with search intent to achieve high rankings on Google.
Types of Search Intent
- Navigational Intent: The searcher is looking for a specific page such as "Facebook login" or "SEO Reddit."
- Informational Intent: The searcher wants to learn something, like "How to increase my website organic traffic."
- Commercial Intent: The searcher is researching products or services, such as "Best smartphones 2024."
- Transactional Intent: The searcher is ready to buy something, like "Buy running shoes." or "Book a roofing service"
Navigational Intent
Navigational intent is when users are looking to navigate to a specific website or page. They already know where they want to go and use search engines to get there.
For instance, someone searching "Facebook login" wants to go directly to Facebook’s login page or "SEO Reddit" to visit a specific forum.
These searches are easy to rank for since searchers include your brand in the search phrase. All you have to do is to make sure your landing pages are optimised and accessible to capture this intent effectively.
Informational Intent
Informational intent is when users seek information or answers to their questions. These searches do not have a commercial intent; the user simply wants to learn or understand something.
An example is "How to increase my website organic traffic."
Businesses can capture informational search intent by creating detailed, informative content that answers common questions or provides valuable insights. Blog posts, how-to guides, and educational articles are effective for this purpose.
Although clicks from informational content are less likely to convert immediately, there are significant benefits:
- Lead Nurturing: Include a small funnel within the informational content to encourage users to subscribe to an email newsletter or direct them to relevant offerings such as eBooks or webinars.
- Brand Authority: When users find your content useful, it builds trust and establishes your brand as an authority in your field, which can lead to higher rankings on search engines.
- Increased Engagement: High-quality informational content can keep users on your site longer, reducing bounce rates and improving overall user engagement metrics.
- Future Conversions: Users who initially visit for information may return later for your products or services, having already formed a positive impression of your brand.
Commercial Intent
Commercial intent lies between informational and transactional intent. Users are considering a purchase and researching their options. They seek information closely connected to taking action but are not ready to buy yet.
For example, "Best smartphones 2024."
To target commercial intent, businesses should create comparison articles, product reviews, and buying guides. These types of content help users in their decision-making process by providing detailed information on features, pros, and cons of various products or services.
By doing so, businesses can influence potential customers and guide them towards their offerings.
Transactional Intent
Transactional intent is when users are ready to make a purchase. These searches often include terms like "buy," "order," or "purchase."
An example is "Buy running shoes."
Most top rankers on these search terms are E-commerce websites that focus on making the purchasing process as smooth as possible, from product selection to checkout.
Services, on the other hand, also cater to transactional intent by making sure that their booking or appointment systems are straightforward and user-friendly. For instance, a search for "Book a roofing service" should lead to a seamless booking process on the service provider's website, enhancing the user's experience and increasing the likelihood of conversion.
Note: Some Keywords Can Have Multiple Intents
There are some cases in which a keyword has multiple intents.
For example, the keyword "Medical Virtual Assistant" could be used by a medical professional or business looking to hire a virtual assistant. Alternatively, it could be used by a medical virtual assistant looking for a job.
In such cases, Google often provides a mix of results to satisfy different user intents.
For the keyword "Medical Virtual Assistant," content could include job listings for virtual assistants, as well as information on how to hire a medical virtual assistant.
Search engines always want to make sure that users find relevant information regardless of their specific intent, improving the chances of engagement and conversions.
Search Intent and User Journey Mapping
The user journey consists of several stages, from awareness to decision-making, and search intent varies at each stage.
1. Awareness Stage
At this stage, users are seeking information to understand a problem or a concept. They are not yet considering specific solutions. Keywords used in this stage are usually informational.
For example, "What is a virtual assistant?" Here, the user is trying to learn about virtual assistants and what they do.
2. Consideration Stage
In the consideration stage, users are comparing different solutions to their problems. They have identified their needs and are now evaluating options. Keywords in this stage are more evaluative.
For example, "Benefits of hiring a virtual assistant." Users want to understand the advantages and how a virtual assistant can help them.
3. Decision Stage
Users in the decision stage are ready to make a purchase or take a specific action. They have done their research and are looking for the best provider. Keywords in this stage are transactional.
For example, "Hire a virtual assistant in Sydney." The user is now looking for a specific service to fulfil their need.
Mapping search intent to the user journey helps businesses create targeted content that meets users' needs at each stage.
Want to Improve Your Website's SEO?
Marketix Digital deeply understands not only search intent but all aspects of SEO. As a leading Sydney-based SEO agency, we are committed to helping you achieve your digital marketing goals. Our team of experts is well-versed in the latest SEO techniques and strategies to make sure your website ranks highly on search engines.
We offer comprehensive SEO services and our proven track record is demonstrated through numerous SEO case studies, showcasing significant improvements in organic traffic and search rankings for our clients.
Contact us today to get started on your journey to SEO success.

Free Download SEO Book
Download our 24-page SEO book to learn:
- How SEO Really Works
- How to Rank #1
- Content & SEO
- Choosing an SEO Agency
Thank you!
You have successfully joined our subscriber list.






