- Home
- > The Marketix Blog
- > SEO
A Technical Guide to DNS and SEO

There's a lesser-known factor that significantly impacts SEO: the Domain Name System (DNS). It's so crucial yet often overlooked by many marketers and webmasters.
Did you know? 91% of malware uses DNS for command and control, which underscores the importance of a solid DNS setup.
From an SEO perspective, DNS can directly affect your website’s visibility and performance. Slow DNS resolution can increase page load times, leading to higher bounce rates and lower search engine rankings.
Now that you know the important role DNS plays in SEO, it's time to dive deeper. From understanding how DNS works to learning how to optimise it for better performance, this guide covers everything you need.
What is DNS?
The Domain Name System (DNS) is the backbone of the internet, translating human-readable domain names into IP addresses that computers use to identify each other.
Without DNS, browsing the web would be cumbersome, as users would need to remember numerical IP addresses instead of simple domain names.
Essentially, DNS acts as the internet's phone book, making sure that you reach the correct website when entering a URL.
DNS comprises several key components:
- Domain names
- IP addresses
- DNS servers
Each domain name corresponds to an IP address, and DNS servers manage this mapping. They are like communicating with each other to direct users to the correct IP address, enabling seamless internet navigation.
How does DNS work?
The DNS resolution process involves several steps.
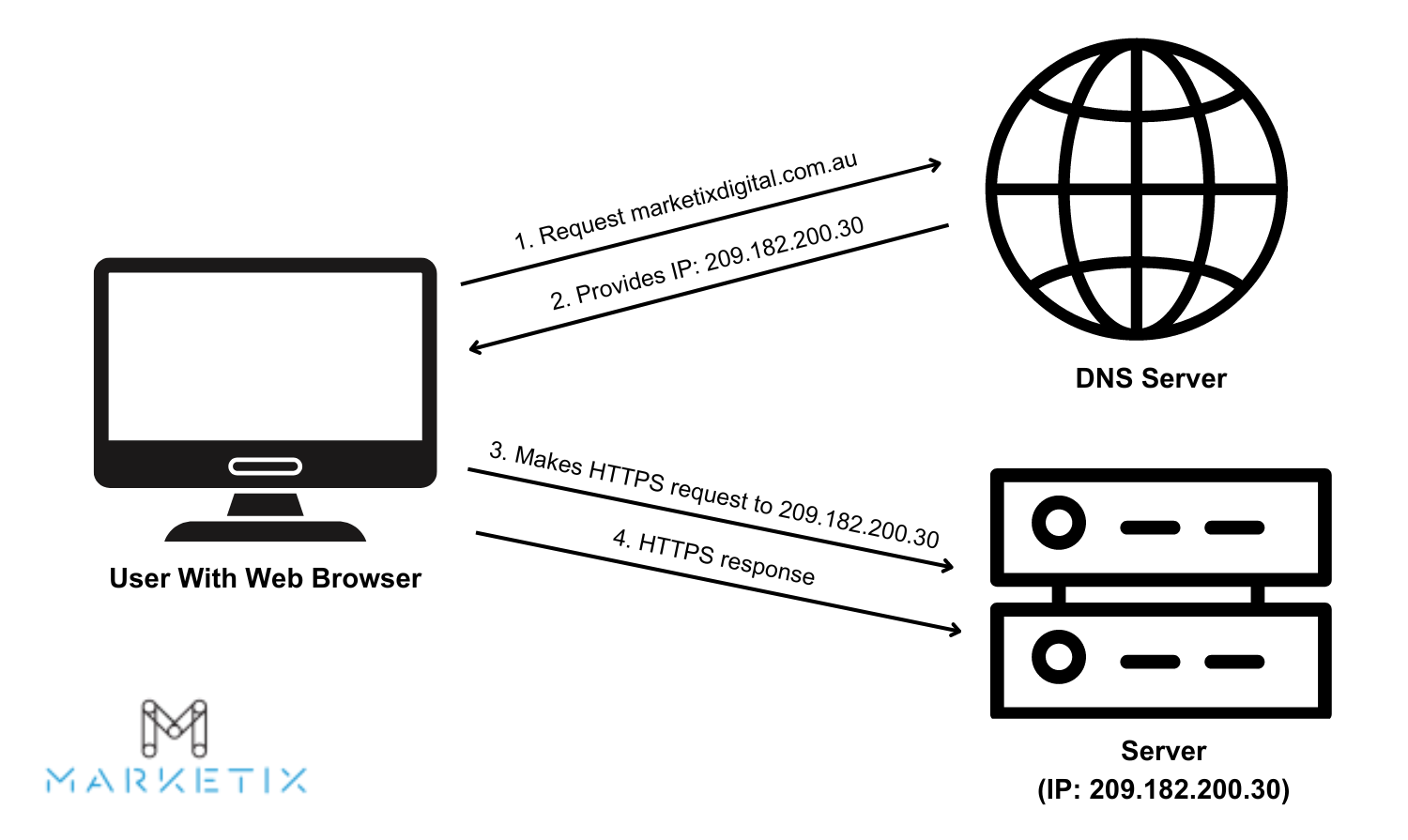
When a user enters a domain name, the browser first checks its local cache. If the information isn't cached, the query is sent to a recursive DNS server. This server may also check its cache before querying a root DNS server, which directs the query to the appropriate top-level domain (TLD) server.
The TLD server then points to the authoritative DNS server for the specific domain, which provides the corresponding IP address.
There are two main types of DNS queries: recursive and iterative.
In a recursive query, the DNS server is responsible for retrieving the complete answer by querying other servers. In contrast, an iterative query involves the DNS server returning the best answer it can, typically a referral to another server, and leaving it to the requesting party to continue the search.
DNS records play an important role in this system. The most common types include:
- A Records: Map domain names to IPv4 addresses.
- CNAME Records: Alias one domain name to another.
- MX Records: Direct email to mail servers.
- TXT Records: Provide text information to sources outside the domain.
These components and processes are essential for optimising DNS for better SEO performance.
DNS and Website Performance
DNS plays a huge role in website speed, directly impacting user experience and SEO performance.
Slow DNS lookup times can significantly increase page load times, leading to higher bounce rates and lower search engine rankings.
Research shows that a delay of just one second in page load time can result in a 7% reduction in conversions.
Tools such as Google PageSpeed Insights and GTmetrix are invaluable for measuring DNS performance, providing detailed insights into how DNS lookup times affect overall website speed.
Optimising DNS performance is important for maintaining a fast and reliable website. Using faster DNS providers can dramatically reduce lookup times. Services like Cloudflare and Google Public DNS are popular choices known for their speed and reliability.
DNS caching is another effective strategy, allowing frequently accessed domain information to be stored locally, reducing the need for repeated lookups. This not only speeds up access times but also reduces the load on DNS servers.
Reducing the number of DNS lookups can further enhance website performance. Each DNS lookup adds to the time it takes for a page to load. Minimising the number of external resources, such as third-party scripts and images, can decrease the number of DNS queries required.
Consolidating resources and using efficient coding practices will help streamline DNS resolution, resulting in faster page loads and a better user experience.
How About the Impact of DNS on SEO?
Direct Impact of DNS on SEO
Google considers page load speed as a ranking factor, and slow DNS resolution can add precious seconds to load times. A fast DNS response ensures quicker page loads, contributing to better SEO performance.

Moreover, the uptime and reliability of your DNS provider are important to look at as well. Frequent downtime or DNS failures can lead to site inaccessibility, negatively impacting your search rankings and leading to potential penalties from search engines.
Indirect Impact of DNS on SEO
Slow DNS lookups can lead to higher bounce rates as users abandon sites that take too long to load.
With Google's mobile-first indexing, the speed of mobile site access has become even more critical.
Just so you know: Mobile users are particularly sensitive to delays.
That said, DNS speed is a vital component of mobile SEO strategies.
Common DNS Issues and Their SEO Implications
DNS Misconfigurations
Common issues include incorrect DNS records, such as A or CNAME records pointing to wrong IP addresses, or missing MX records affecting email deliverability.
These misconfigurations can lead to website inaccessibility, slow load times, and poor user experience, all of which negatively impact search rankings.
Diagnosing these issues often involves using tools like DNSChecker and intoDNS to identify errors in DNS records.
DNS Downtime
Causes include server failures, DDoS attacks, and network issues.
When DNS servers are down, users cannot access your website, resulting in lost traffic and potential revenue.
Frequent downtime can lead to search engines devaluing your site, reducing its visibility in search results.
Preventative measures include using reliable DNS providers with strong uptime guarantees, implementing DNS failover systems, and regularly monitoring DNS performance. Contingency planning, such as having backup servers, can also mitigate the impact of unexpected downtime.
DNS Propagation Delays
DNS propagation delays occur when changes to DNS records take time to update across the internet.
This delay can range from a few hours to 48 hours, depending on various factors like TTL (Time to Live) settings.
During propagation, users may experience difficulty accessing your website, leading to a temporary drop in traffic and potential SEO impact.
To minimise these effects, it is important to plan DNS changes during low-traffic periods and lower the TTL settings before making changes. This reduces the time required for new DNS information to propagate globally, making sure of quicker updates and minimal disruption.
Need Help with DNS and SEO?
Managing DNS and achieving optimal SEO performance can be complex and time-consuming.
We, at Marketix Digital, specialise in handling technical SEO-related tasks. Our team of experts will make sure that your DNS is configured correctly, optimised for speed, and secured against potential threats.
We use advanced tools and strategies to monitor, diagnose, and resolve any DNS issues, keeping your site accessible and fast.
Don't let technical challenges hold back your online success. Contact us today, and let us handle the complexities of DNS and SEO, so you can focus on growing your business.

Free Download SEO Book
Download our 24-page SEO book to learn:
- How SEO Really Works
- How to Rank #1
- Content & SEO
- Choosing an SEO Agency
Thank you!
You have successfully joined our subscriber list.






