- Home
- > The Marketix Blog
- > SEO
How to Use Canonical Tags Effectively

It should be a fundamental aspect of your SEO strategy, yet canonical tags often remain misunderstood or overlooked.
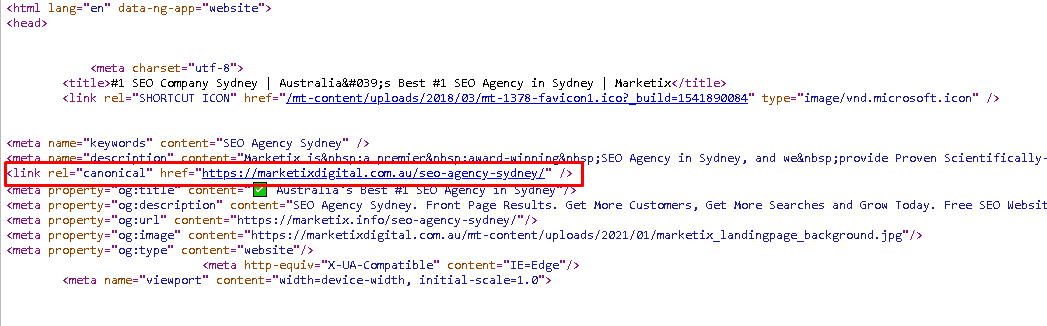
Canonical tags, or canonical links, help search engines understand which version of a URL represents the master copy of a page. This can prevent duplicate content issues and consolidate link signals for better SEO performance.
Implementing canonical tags correctly can have a significant impact on your website’s search rankings. Let's dive into what canonical tags are and why they are so important for your SEO efforts.
What Are Canonical Tags?
Canonical tags are HTML elements that help search engines identify the preferred version of a webpage when multiple URLs have identical or very similar content.
By specifying the canonical URL, you instruct search engines to consider that URL as the master copy, consolidating any SEO value and preventing duplicate content issues.
For example, an online store might have a product accessible through several URLs:
- www.example.com/shoes/sneakers?color=red
- www.example.com/sneakers?color=red
- www.example.com/products/sneakers/red
Using a canonical tag, you can indicate which URL should be treated as the primary version. In this case, you might choose www.example.com/products/sneakers/red as the canonical URL.
Proper use of canonical tags is important for maintaining a clean and effective SEO strategy.
Why Are Canonical Tags Important in SEO?
Imagine losing search traffic because search engines can't figure out which page to rank. That's where canonical tags come in.
They simplify the decision-making process for search engines, ensuring that the right page gets the attention it deserves.
Should every page have a canonical tag? Not necessarily, but it's a best practice.
Including a canonical tag on each page helps maintain consistency across your site. It guides search engines even when duplicate content isn't immediately apparent. This proactive approach can prevent potential SEO issues before they arise.
The impact of canonical tags on SEO can be significant.
But consider an e-commerce site with multiple product variants. Without canonical tags, search engines might treat each variant as a separate page, splitting the link equity among them. Specifying a canonical URL consolidates this equity, boosting the primary page's ranking potential.
Another scenario involves syndicated content. If your articles are republished on other sites, using canonical tags will make sure that the source receives proper credit, preserving its search visibility and authority.
Step-by-Step Implementation Guide
Step 1: Identify Duplicate Content
Begin by auditing your website to identify pages with duplicate or very similar content. Tools like Screaming Frog can help you find these duplicates. Look for pages with identical titles, meta descriptions, or body content.
We are big fans of Screaming Frog as it makes everything done fast and easy.
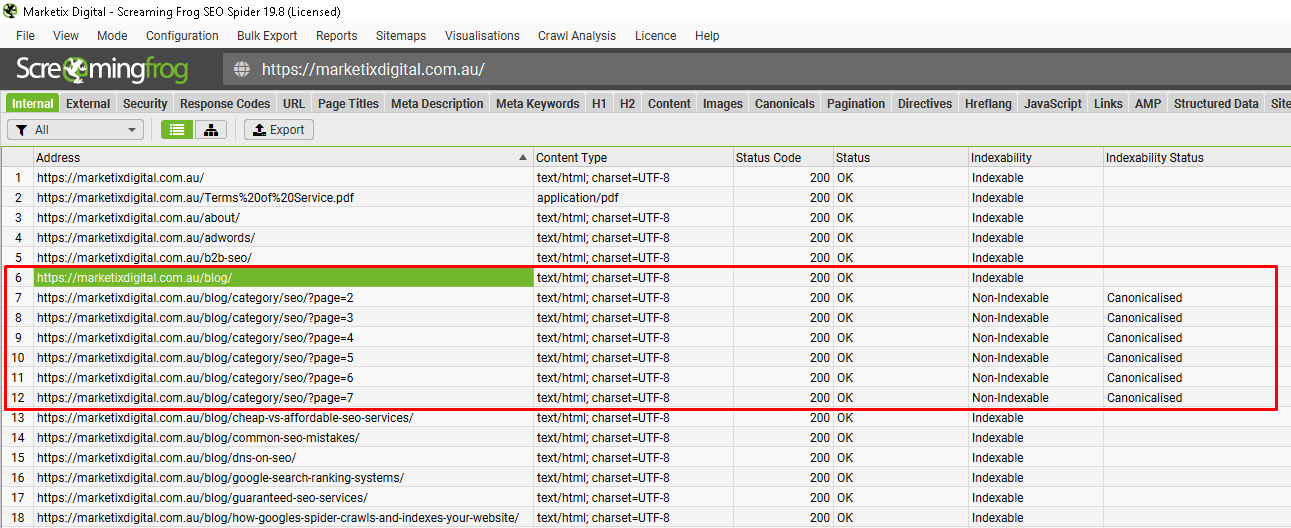
Pro Tip: Regularly schedule content audits to catch duplicates early and maintain a clean site structure.
Step 2: Choose the Canonical URL
Determine the primary version of each duplicate page. This URL should be the one you want search engines to index and rank. Consider factors like user experience, URL structure, and existing backlinks when making your choice.
Use short, descriptive URLs for your canonical tags. They should be easy to read and remember.
Step 3: Add the Canonical Tag
Add the canonical tag to the HTML head section of the duplicate pages. The tag should point to the chosen primary URL. The format looks like this:
<link rel="canonical" href="https://www.example.com/preferred-page" />
Step 4: Verify Implementation
After adding canonical tags, verify their implementation. Use tools like Google Search Console or Moz to make sure that search engines recognise the canonical URLs correctly. Check for any errors or warnings related to your canonical tags.
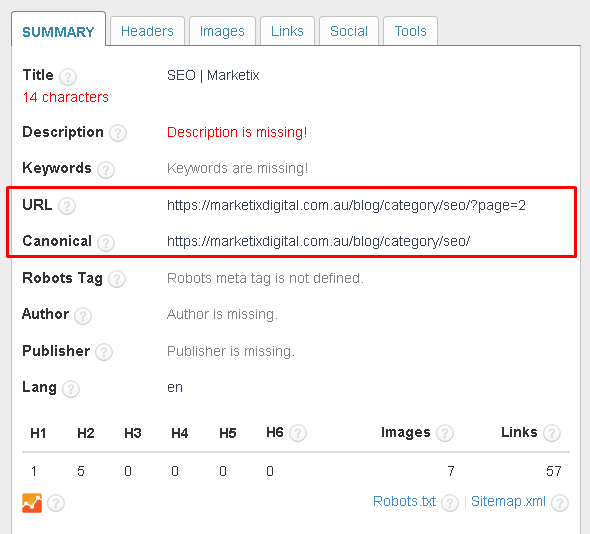
You can also use browser extensions like the SEO Meta in 1 Click to quickly check the canonical tags on your pages.
Step 5: Monitor and Adjust
Monitor the performance of your canonical tags over time. Look for changes in search rankings, traffic patterns, and crawl reports. If you notice issues, revisit your canonical tag implementation and make necessary adjustments.
Step 6: Use Rel-Canonical HTTP Header
For non-HTML content like PDFs or images, use the rel-canonical HTTP header to specify the canonical URL. This will make sure that all types of content on your site are properly indexed and ranked.
The best approach would be to Implement rel-canonical headers in server-side configurations to cover all bases, especially for large sites with varied content types.
Step 7: Implement Cross-Domain Canonical Tags
If you syndicate content across multiple domains, use cross-domain canonical tags to indicate the source.
Step 8: Regularly Update Canonical Tags
As your site grows and changes, regularly update your canonical tags to reflect the current structure and content priorities.
Pro Tip: Include canonical tag reviews in your regular SEO maintenance checklist to keep your site optimised.
Following these steps will make sure that your canonical tags are effectively implemented, helping search engines understand your content hierarchy and improving your site's SEO performance.
Common Mistakes to Avoid with Canonical Tags
Even with the best intentions, mistakes can occur during the implementation of canonical tags. Here are some common errors to watch out for:
- Canonicalising the Wrong URL: Ensure that the chosen canonical URL is the most relevant and authoritative version of the page. Selecting a less relevant URL can dilute your SEO efforts.
- Not Including Canonical Tags on Every Page: While not every page needs a canonical tag, missing them on key pages can lead to confusion and duplicate content issues. It’s better to be consistent and include canonical tags site-wide.
- Pointing Canonical Tags to Non-Canonical Pages: Make sure that canonical tags always point to the correct, canonical version of the page. Avoid circular references where pages point to each other as canonical.
- Using Multiple Canonical Tags: Only one canonical tag should be present per page. Multiple tags can confuse search engines and lead to improper indexing.
- Ignoring Case Sensitivity and Trailing Slashes: URLs are case-sensitive, and inconsistencies with trailing slashes can create duplicate content issues. Ensure uniformity in your canonical tags.
Advanced Canonical Tag Techniques
For those looking to go beyond the basics, here are some advanced techniques to enhance your SEO strategy with canonical tags:
1. Pagination Handling
For paginated content, it's crucial to use canonical tags correctly to avoid duplicate content issues while ensuring that each page in the series is indexed. Use the <link rel="prev"> and <link rel="next"> tags in combination with canonical tags to guide search engines through paginated series.
Example:
- <link rel="canonical" href="https://www.example.com/article/page/1" />
- <link rel="prev" href="https://www.example.com/article/page/2" />
- <link rel="next" href="https://www.example.com/article/page/3" />
2. Canonical Tags for Parameterized URLs
Websites that use URL parameters for sorting, filtering, or tracking can benefit greatly from canonical tags. Specify the canonical URL for parameterized pages to prevent dilution of SEO value.
Example:
<link rel="canonical" href="https://www.example.com/category/page" />
3. Handling Canonical Tags in Multi-Language Sites
For websites that offer content in multiple languages, using canonical tags along with hreflang tags can be beneficial. This ensures that each language version of a page is correctly indexed while still consolidating SEO signals for the primary content.
Example:
- <link rel="canonical" href="https://www.example.com/en/page" />
- <link rel="alternate" hreflang="es" href="https://www.example.com/es/page" />
- <link rel="alternate" hreflang="fr" href="https://www.example.com/fr/page" />
Canonical Tags and Analytics
Canonical tags can also impact your website analytics. Here’s how to ensure accurate data tracking:
1. Consistent Tracking URLs
Make sure that your analytics software is configured to recognize canonical URLs as the primary source. This prevents inflated pageview counts from duplicate URLs.
2. UTM Parameters
When using UTM parameters for tracking, be cautious with canonical tags. Ensure that the canonical URL does not include UTM parameters to avoid splitting the SEO value.
Example:
<link rel="canonical" href="https://www.example.com/page" />
Ready to Optimize Your SEO Strategy?
If you're looking for the best Sydney SEO agency to handle all your SEO needs including these technical errors, look no further.
We specialise in delivering tailored SEO solutions that drive real results. Our team of experts understands the intricacies of canonical tags and other advanced SEO techniques.
Whether you're dealing with duplicate content issues, managing SEO on a complex e-commerce site, or looking to improve your search rankings, we have the experience and expertise to help you succeed.
We offer comprehensive SEO audits, strategic implementations, and ongoing support to keep your site optimised and ahead of the competition.

Free Download SEO Book
Download our 24-page SEO book to learn:
- How SEO Really Works
- How to Rank #1
- Content & SEO
- Choosing an SEO Agency
Thank you!
You have successfully joined our subscriber list.






